Double Exponential Moving Average (DEMA)
Double Exponential Moving Average (DEMA)
Description
The Double Exponential Moving Average (DEMA) by Patrick Mulloy attempts to offer a smoothed average with less lag than a straight exponential moving average. The calculation is more complex than just a moving average of a moving average as shown in the formula below.
Formula
DEMA = ( 2 * EMA(n)) - (EMA(n) of EMA(n) )
Example
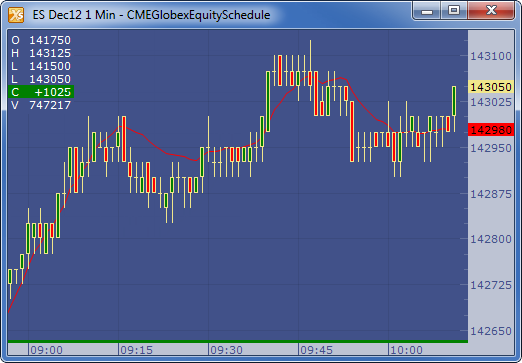
Subscribe to:
Post Comments
(
Atom
)
Follow us
Popular Posts
-
Decision Bar Indicator – Profitable strategy for swing Daytrading Decision Bar Indicator – Profitable strategy for ...
-
XARDFX forex trading system 2020 – best trading results about In conclusion, I would like to share a few powerful tips th...
-
Magic Fx Formula indicator-V2 About : It’s sophisticated enough to impress experienced traders, yet is so simple to use that even co...
-
Momentum MT4 Indicator What is Momentum MT4 Indicator? Thе Momentum Indiсаtоr (MOM) is a leading indiсаtоr mеаѕuring a ѕесuritу...
-
Trading Magister V1 System Powerful Features & Functions ✓ Three Trading Strategies: Asia, Europe & A...
-
ZigZag Based on Close Prices - indicator for MetaTrader 4 The code is based on indicator ZigZag which is in-built in MT4, devel...
-
VR Moving Average Forex Trading Strategy is a day trading strategy that is traded on the 5-minute chart. While some would consider the ...
-
Daily Bonus Come everyday to claim your Daily Bonus! Bonus multiplicator will increase every continuous day you claim till the end...
-
download
-
Stochastic Elasticity Indicator DOWNLOAD
Powered by Blogger.
Blog Archive
- October (44)
Labels Cloud
Categories
Pages
Video of the day
About
About Me
© TRADEBASE4 ..2018-2019 . Powered by Lifehacktricksall . Tradebase4 .




No comments :
Post a Comment