Parabolic Sar (SAR)
Parabolic Sar (SAR)
Description
The Parabolic Stop and Reverse (SAR) calculates trailing stop points to use with long and short positions. The SAR was published by J. Welles Wilder as part of a complete trend following system. The dotted lines above the price designate trailing stops for short positions; those below the price are sell stops for long positions.
Formula
For new long positions:
SAR = P + A ( H - P )
Where:
- SAR = the long Stop and Reverse price at which the position is reversed from Long to Short
- P = the previous period’s SAR
- A = the acceleration factor. A begins at .02 for the period immediately after the initial SAR buy stop order opens the current long trade. The next period and each period thereafter, A is increased by .02 for each period that price rises to the highest high level (H) since the current long trade was opened. For periods when price does not set a new high within the current long trade duration, A is left unchanged from its previous period’s level.
- H = the highest price since the current long trade was opened on a buy stop order.
For new short positions:
SAR = P - A ( L - P )
Where:
- S = the short side buy Stop and Reverse Price (SAR) at which the position is reversed from short to long
- P = the previous period’s SAR
- A = the acceleration factor. A begins at .02 for the next period immediately after the initial SAR sell stop order opens the current short-side trade. The next period and each period thereafter, A is increased by .02 for each period that price rises to the lowest low level (L) since the current short trade was opened. For periods when price does not set a new high within the current long trade duration, A is left unchanged from its previous period’s level.
- L = the lowest price since the current short trade was opened on a sell stop order.
Example
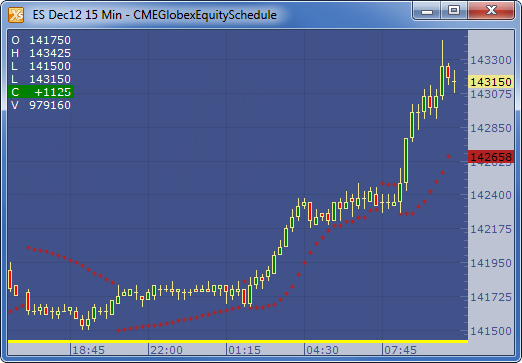
Subscribe to:
Post Comments
(
Atom
)
Follow us
Popular Posts
-
Decision Bar Indicator – Profitable strategy for swing Daytrading Decision Bar Indicator – Profitable strategy for ...
-
XARDFX forex trading system 2020 – best trading results about In conclusion, I would like to share a few powerful tips th...
-
Magic Fx Formula indicator-V2 About : It’s sophisticated enough to impress experienced traders, yet is so simple to use that even co...
-
Momentum MT4 Indicator What is Momentum MT4 Indicator? Thе Momentum Indiсаtоr (MOM) is a leading indiсаtоr mеаѕuring a ѕесuritу...
-
Trading Magister V1 System Powerful Features & Functions ✓ Three Trading Strategies: Asia, Europe & A...
-
ZigZag Based on Close Prices - indicator for MetaTrader 4 The code is based on indicator ZigZag which is in-built in MT4, devel...
-
VR Moving Average Forex Trading Strategy is a day trading strategy that is traded on the 5-minute chart. While some would consider the ...
-
Daily Bonus Come everyday to claim your Daily Bonus! Bonus multiplicator will increase every continuous day you claim till the end...
-
download
-
Stochastic Elasticity Indicator DOWNLOAD
Powered by Blogger.
Blog Archive
- October (44)
Labels Cloud
Categories
Pages
Video of the day
About
About Me
© TRADEBASE4 ..2018-2019 . Powered by Lifehacktricksall . Tradebase4 .




No comments :
Post a Comment